This guide is for developers who want to build an FTSOv2 application using either Foundry or Hardhat.
Hardhat is a development tool that simplifies writing, testing and deploying smart contracts on Ethereum. (Recommended for Beginners)
If you've never used Hardhat before, complete these steps first.
# Check if Node.js is already installed
node --version
# If not installed, download from nodejs.org
# Or use a package manager like:
# Windows: chocolatey install nodejs
# Mac: brew install nodeNode.js is the environment that runs JavaScript code on your computer. You need version v22.21.1 to work with Hardhat.
# Install Hardhat globally on your computer
npm install -g hardhat
# Verify installation
npx hardhat --versionThis installs Hardhat so you can use it in any project. The -g flag means “globally“ - available everywhere on your computer.

# Visit the Coston2 faucet to get test tokens:
# https://faucet.flare.network/
# You'll need testnet FLR for deployment gas feesTestnet tokens are free cryptocurrency used for testing. You need them to pay for transaction fees when deploying contracts. They have no real value and are only for practice.
Instead of building everything from scratch, we'll use Flare's pre-built starter template:
# Download the Flare starter project
git clone https://github.com/flare-foundation/flare-hardhat-starter.git
# Move into the project folder
cd flare-hardhat-starter
# Install all the required tools
yarn installThis downloads a project that already has Hardhat, TypeScript, and all the Flare-specific tools configured. It's like getting a pre-built kitchen instead of buying each appliance separately.

This is what you should see when the setup completes
# Create environment file
cp .env.example .env
# Open the file in your text editor
# Add your private key and RPC URLNever share your private keys. Never put private keys in source code. Never commit private keys to Git. The .env file is automatically ignored by Git to keep your keys safe.
Your .env file should look like this (use your own values):
PRIVATE_KEY=your_private_key_here
COSTON2_RPC_URL=https://coston2-api.flare.network/ext/C/rpc
FLARE_RPC_URL=https://flare-api.flare.network/ext/C/rpcIf you do not have a private key visit Get Started in flare docs
Update your hardhat.config.ts file to use the Shanghai EVM version:
module.exports = {
solidity: {
version: "0.8.27",
settings: {
evmVersion: "shanghai",
optimizer: {
enabled: true,
runs: 200,
},
},
},
};The Shanghai EVM version includes the latest Ethereum features and optimizations. The optimizer makes your contract smaller and cheaper to deploy by simplifying the code.
Create a new file at contracts/FTSOV2Consumer.sol and let's build it piece by piece:
import {TestFtsoV2Interface} from "@flarenetwork/flare-periphery-contracts/coston2/TestFtsoV2Interface.sol";
import {ContractRegistry} from "@flarenetwork/flare-periphery-contracts/coston2/ContractRegistry.sol";These are like importing libraries in other languages. They give us pre-built functions to talk to FTSOv2.
bytes21 public constant flrUsdId = 0x01464c522f55534400000000000000000000000000; // FLR/USD
bytes21[] public feedIds = [
bytes21(0x01464c522f55534400000000000000000000000000), // FLR/USD
bytes21(0x014254432f55534400000000000000000000000000), // BTC/USD
bytes21(0x014554482f55534400000000000000000000000000) // ETH/USD
];These special codes are like product IDs for each price feed. Each cryptocurrency pair has its own unique ID.
function getFlrUsdPrice() external view returns (uint256, int8, uint64) {
TestFtsoV2Interface ftsoV2 = ContractRegistry.getTestFtsoV2();
return ftsoV2.getFeedById(flrUsdId);
}This function does three things: 1. Connects to FTSOv2, 2. Asks for the FLR/USD price, 3. Returns the price, decimal places, and timestamp.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity >=0.8.0 <0.9.0;
import {TestFtsoV2Interface} from "@flarenetwork/flare-periphery-contracts/coston2/TestFtsoV2Interface.sol";
import {ContractRegistry} from "@flarenetwork/flare-periphery-contracts/coston2/ContractRegistry.sol";
contract FtsoV2Consumer {
bytes21 public constant flrUsdId = 0x01464c522f55534400000000000000000000000000;
bytes21[] public feedIds = [
bytes21(0x01464c522f55534400000000000000000000000000), // FLR/USD
bytes21(0x014254432f55534400000000000000000000000000), // BTC/USD
bytes21(0x014554482f55534400000000000000000000000000) // ETH/USD
];
function getFlrUsdPrice() external view returns (uint256, int8, uint64) {
TestFtsoV2Interface ftsoV2 = ContractRegistry.getTestFtsoV2();
return ftsoV2.getFeedById(flrUsdId);
}
function getMultiplePrices() external view returns (uint256[] memory, int8[] memory, uint64) {
TestFtsoV2Interface ftsoV2 = ContractRegistry.getTestFtsoV2();
return ftsoV2.getFeedsById(feedIds);
}
}npx hardhat compileCompiling converts your human-readable Solidity code into bytecode that the blockchain can understand. It's like translating a recipe into instructions a robot chef can follow.
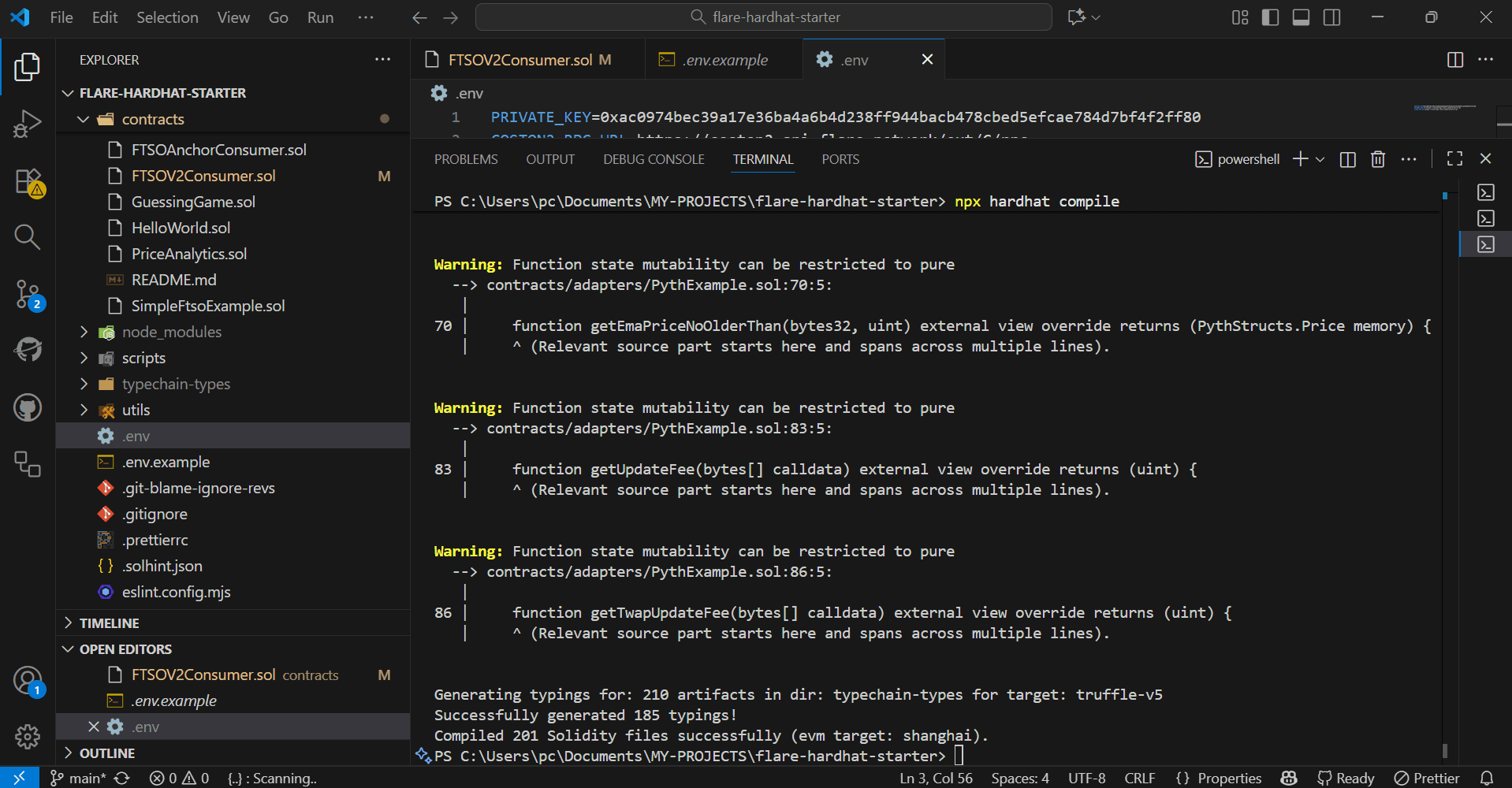
You'll see this when your contract compiles without errors
Let's create a simple test to make sure our contract actually returns price data: test/price.test.js file
import { expect } from "chai";
import { ethers } from "hardhat";
describe("FtsoV2Consumer", function () {
let ftsoV2Consumer: any;
beforeEach(async function () {
const FtsoV2ConsumerFactory = await ethers.getContractFactory("FtsoV2Consumer");
ftsoV2Consumer = await FtsoV2ConsumerFactory.deploy();
await ftsoV2Consumer.waitForDeployment();
});
it("Should return the FLR/USD price, decimals, and timestamp", async function () {
const result = await ftsoV2Consumer.getFlrUsdPrice();
console.log("
=== getFlrUsdPrice ===");
console.log("Price:", result[0].toString());
console.log("Decimals:", result[1].toString());
console.log("Timestamp:", result[2].toString());
expect(result[0]).to.be.a("bigint");
expect(result[0]).to.be.gt(0);
expect(result[1]).to.be.a("bigint");
expect(result[2]).to.be.a("bigint");
expect(result[2]).to.be.gt(0);
});
it("Should return the FLR/USD price in Wei and timestamp", async function () {
const result = await ftsoV2Consumer.getFlrUsdPriceWei();
console.log("
=== getFlrUsdPriceWei ===");
console.log("Price in Wei:", result[0].toString());
console.log("Timestamp:", result[1].toString());
expect(result[0]).to.be.a("bigint");
expect(result[0]).to.be.gt(0);
expect(result[1]).to.be.a("bigint");
expect(result[1]).to.be.gt(0);
});
it("Should return current feed values for multiple feeds", async function () {
const result = await ftsoV2Consumer.getFtsoV2CurrentFeedValues();
console.log("
=== getFtsoV2CurrentFeedValues ===");
console.log("Feed Values:", result[0].map((v: bigint) => v.toString()));
console.log("Decimals:", result[1].map((d: bigint) => d.toString()));
console.log("Timestamp:", result[2].toString());
expect(result[0]).to.be.an("array");
expect(result[0]).to.have.lengthOf(3);
expect(result[1]).to.be.an("array");
expect(result[1]).to.have.lengthOf(3);
expect(result[2]).to.be.a("bigint");
expect(result[2]).to.be.gt(0);
});
it("Should have the correct constant flrUsdId", async function () {
const flrUsdId = await ftsoV2Consumer.flrUsdId();
console.log("
=== flrUsdId ===");
console.log("FLR/USD ID:", flrUsdId);
expect(flrUsdId).to.equal("0x01464c522f55534400000000000000000000000000");
});
it("Should have the correct initial feedIds array", async function () {
const feedId1 = await ftsoV2Consumer.feedIds(0);
const feedId2 = await ftsoV2Consumer.feedIds(1);
const feedId3 = await ftsoV2Consumer.feedIds(2);
console.log("
=== feedIds ===");
console.log("Feed 1:", feedId1);
console.log("Feed 2:", feedId2);
console.log("Feed 3:", feedId3);
expect(feedId1).to.equal("0x01464c522f55534400000000000000000000000000");
expect(feedId2).to.equal("0x014254432f55534400000000000000000000000000");
expect(feedId3).to.equal("0x014554482f55534400000000000000000000000000");
});
});Lines 1-2: Import testing framework (Chai) and Hardhat Ethereum library
Lines 4-5: Define test suite for the FtsoV2Consumer contract
Lines 6-10: Before each test, deploy a fresh contract instance to ensure test isolation
Lines 12-24: Test that retrieves FLR/USD price data and validates the return types and values
Lines 26-36: Test that gets price in Wei format and verifies the data structure
Lines 38-50: Test that fetches multiple price feeds simultaneously and checks array structures
Lines 52-59: Test that verifies the constant FTSO identifier matches expected format
Lines 61-72: Test that confirms the feed IDs array contains the correct predefined values
Tests let you verify your contract works before spending real money to deploy it. They're like test-driving a car before buying it.
npx hardhat test --network coston2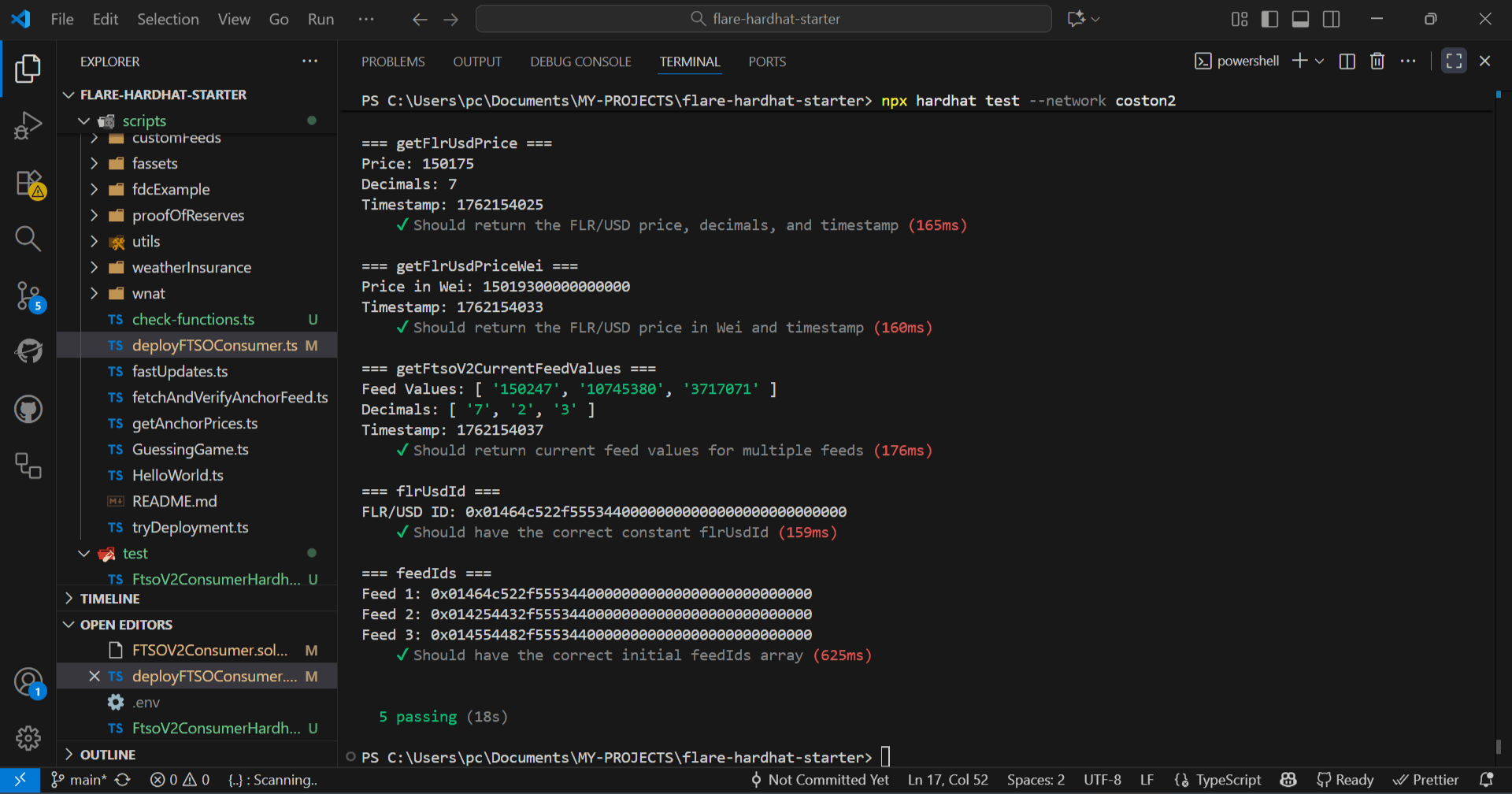
Your tests should show real price data from the Flare network
Create a file called scripts/deployFTSOConsumer.ts with this simple deployment script:
import { ethers } from "hardhat";
async function main() {
console.log("🚀 Deploying and Testing FtsoV2Consumer...");
const [deployer] = await ethers.getSigners();
console.log("📧 Deployer:", deployer.address);
// Deploy contract
const FtsoV2ConsumerFactory = await ethers.getContractFactory("FtsoV2Consumer");
const contract = await FtsoV2ConsumerFactory.deploy();
await contract.waitForDeployment();
const address = await contract.getAddress();
console.log("✅ Contract deployed to:", address);
console.log("
🔍 Testing Contract Functions...");
const [price, decimals, timestamp] = await contract.getFlrUsdPrice();
const [priceWei, timestampWei] = await contract.getFlrUsdPriceWei();
const [feedValues, decimalsArray, feedTimestamp] = await contract.getFtsoV2CurrentFeedValues();
const flrUsdId = await contract.flrUsdId();
const feedId1 = await contract.feedIds(0);
const feedId2 = await contract.feedIds(1);
const feedId3 = await contract.feedIds(2);
}
main().catch(console.error);Lines 1-2: Import Hardhat Ethereum library for deployment and interaction
Lines 4-6: Define the async main function that will run the deployment
Line 8: Log that deployment is starting
Lines 10-11: Grab the deployer wallet and log the address
Lines 13-16: Deploy the FtsoV2Consumer contract and wait until deployment is confirmed
Line 18: Get and log the deployed contract address
Line 20: Begin testing contract functions immediately after deployment
Lines 22-27: Call getFlrUsdPrice, getFlrUsdPriceWei, and getFtsoV2CurrentFeedValues to log their outputs
Lines 28-32: Check constant variables like flrUsdId and the feedIds array
Line 34: Catch and log any errors that occur during deployment
This script deploys your contract to the blockchain and verifies its core functions immediately. It's like sending your code to Flare and opening it right away to make sure everything works.
npx hardhat run scripts/deployFTSOConsumer.ts --network coston2Coston2 is Flare's test network where you can deploy contracts for free using test tokens. It's identical to the real network but uses fake money - perfect for learning!
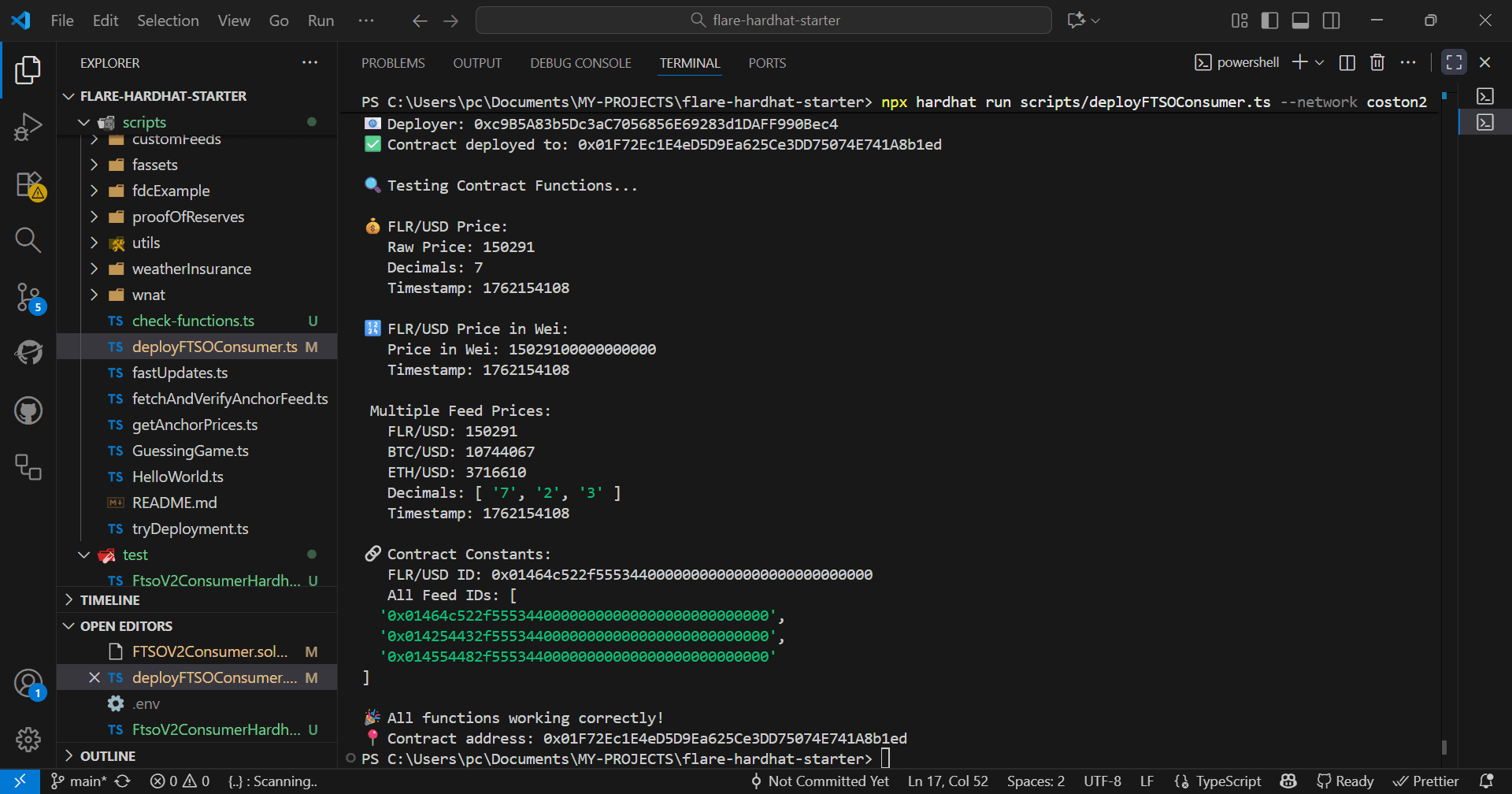
You'll get a contract address that you can use to interact with your deployed contract
You've just built and deployed your first FTSOv2 application! You now have a smart contract running on the Flare network that can read real cryptocurrency prices.
Ready to build something more advanced? Learn how to work with multiple price feeds and advanced FTSO features.